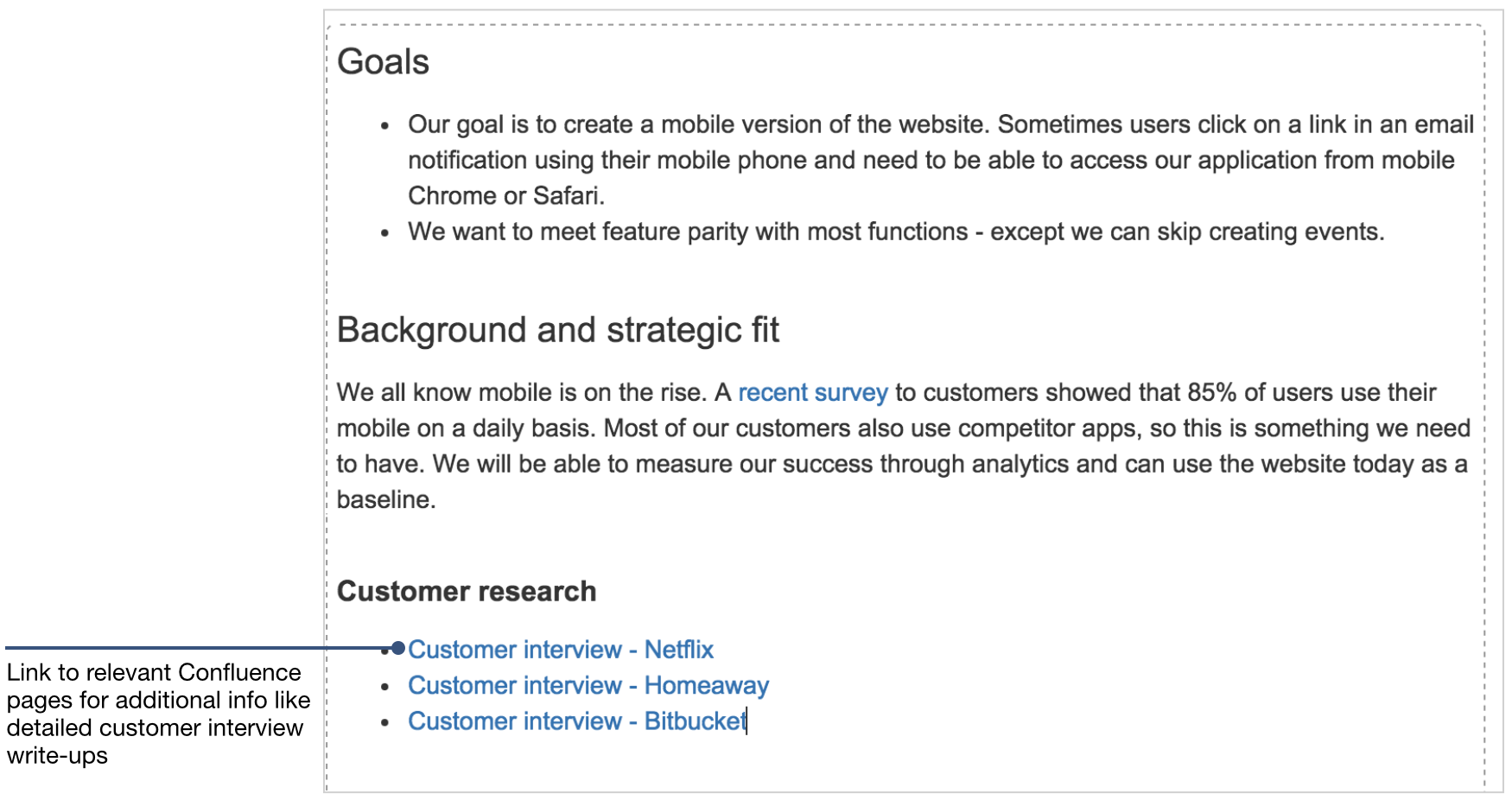
While JIRA has been developed primarily as an issue and project tracker out of the box, you can use JIRA for requirements management in conjunction with Confluence. We will review how Atlassian uses our products for this purpose, as well as provide some relevant resources for further information. Looking for a tool that can support your requirements practices? The following lists might help you finding one. This September 2017 version of our requirements management (RM) tools list contains many updates. It shows that the requirements tool market is currently in a huge transition and transformation phase. Requirements Management and Requirements Modeling are an essential part of controlling complexity, risk, project scope and in un-ambiguously defining the goals and criteria for a successful software or business project. Enterprise Architect, designed as a Requirements Management and Modeling software tool.
Contents • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Overview [ ] The purpose of requirements management is to ensure that an organization documents, verifies, and meets the needs and expectations of its customers and internal or external stakeholders. Requirements management begins with the analysis and elicitation of the objectives and constraints of the organization. Requirements management further includes supporting planning for requirements, integrating requirements and the organization for working with them (attributes for requirements), as well as relationships with other information delivering against requirements, and changes for these. The traceability thus established is used in managing requirements to report back fulfilment of company and stakeholder interests in terms of compliance, completeness, coverage, and consistency. Traceabilities also support change management as part of requirements management in understanding the impacts of changes through requirements or other related elements (e.g., functional impacts through relations to functional architecture), and facilitating introducing these changes. Requirements management involves communication between the project team members and stakeholders, and adjustment to requirements changes throughout the course of the project. To prevent one class of requirements from overriding another, constant communication among members of the development team is critical.
For example, in software development for internal applications, the business has such strong needs that it may ignore user requirements, or believe that in creating, the user requirements are being taken care of. Traceability [ ]. Progecad 2011 Professional Italiano Download Gratis more. Main article: Requirements traceability is concerned with documenting the life of a requirement. It should be possible to trace back to the origin of each requirement and every change made to the requirement should therefore be documented in order to achieve traceability. Even the use of the requirement after the implemented have been deployed and used should be traceable. Requirements come from different sources, like the business person ordering the product, the marketing manager and the actual user. These people all have different requirements for the product.

Using requirements traceability, an implemented feature can be traced back to the person or group that wanted it during the. This can, for example, be used during the development process to prioritize the requirement, determining how valuable the requirement is to a specific user.
It can also be used after the deployment when user studies show that a feature is not used, to see why it was required in the first place. Free Stdf File Converter. Requirements activities [ ].
This article needs additional citations for. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (October 2010) () At each stage in a, there are key requirements management activities and methods. To illustrate, consider a standard five-phase development process with Investigation, Feasibility, Design, Construction and Test, and Release stages. Investigation [ ] In Investigation, the first three are gathered from the users, from the business and from the development team. In each area, similar questions are asked; what are the goals, what are the constraints, what are the current tools or processes in place, and so on.